Cloud Security: Essential Strategies to Protect Your Data in the Cloud
Cloud security is the practice of protecting data, applications, and infrastructure hosted in cloud environments by using technical controls, policies, and continuous oversight. It works by combining encryption, identity and access management, configuration hardening, and monitoring to reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. The primary benefit is sustained confidentiality, integrity, and availability of cloud-hosted assets while helping teams meet compliance and data residency requirements. This article explains practical best practices, how to evaluate secure storage solutions, risk-mitigation strategies like backups and monitoring, and the key trends shaping cloud protection through 2025. Readers will gain concrete implementation steps for access controls and encryption, a comparative framework for choosing public, private, or hybrid storage, and actionable tactics for backup, detection, and incident response. We also cover emerging influences such as AI-driven detection and market shifts that affect how organizations prioritize secure cloud data.
What Are the Best Practices for Cloud Data Security?

Cloud data security rests on layered controls that combine identity management, cryptography, secure configuration, and observability to protect information across lifecycles. Effective implementation reduces attack surface and enables fast detection and recovery, which directly lowers breach impact and compliance risk. Below is a prioritized list of core best practices that teams can adopt to secure cloud data and align with operational needs.
Key cloud data security practices to implement:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Enforce least privilege, role-based access control (RBAC), and multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all accounts.
- Encryption: Protect data in transit (TLS) and at rest (AES or equivalent) with centralized key management and rotation.
- Secure Configuration and Patch Management: Harden images, enforce secure baselines, and apply timely patches to reduce vulnerability exposure.
- Logging and Audit Trails: Collect comprehensive audit logs and retain them securely for detection, forensics, and compliance.
- Immutable Backups and Recovery Testing: Maintain versioned, immutable snapshots and validate restores regularly to ensure resilience.
- Monitoring and Incident Response: Use continuous monitoring, alerting, and well-practiced playbooks for rapid containment and remediation.
These practices form a defensible baseline for secure cloud data. Implementing them leads naturally into specific controls for access and encryption, which are covered next.
| Practice | Implementation | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Access Controls | RBAC, MFA, service account policies | Limits lateral movement and unauthorized access |
| Encryption | TLS in transit, AES at rest, KMS with rotation | Protects confidentiality and reduces data exposure |
| Logging & IR | Centralized logs, SIEM integration, playbooks | Enables rapid detection, investigation, and recovery |
This table summarizes the highest-impact controls and how they translate to operational value. The next sections explain how to implement strong access controls and robust encryption in practice.
How to Implement Strong Access Controls and Authentication
Strong access controls begin by defining clear roles, mapping privileges to job functions, and enforcing multi-factor authentication across all user and service accounts. Start by inventorying identities and service principals, then apply least privilege through RBAC policies and scoped permissions that match operational tasks. Regularly review and remove inactive accounts, rotate credentials for service accounts, and restrict the use of overly permissive roles to reduce risk. Implement just-in-time access for privileged operations and log all administrative actions for auditing and playback, which supports timely investigations. These steps minimize account compromise and prepare teams for scalable, policy-driven access management.
What Encryption Methods Secure Cloud Data Effectively?
Encryption safeguards data by rendering it unreadable without appropriate keys, protecting both data at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized exposure. Use TLS (or stronger) for data in transit and strong symmetric algorithms like AES-256 for data at rest; leverage provider or third-party KMS for centralized key lifecycle management and enforce key rotation. Prefer customer-managed keys when regulatory or residency requirements demand stronger control, and combine envelope encryption with hardware-backed key storage where available. Ensure encryption is applied consistently to storage, databases, backups, and inter-service channels so that cryptographic protections persist across the data lifecycle. Proper key management and rotation policies are essential to maintain cryptographic integrity over time.
Which Secure Cloud Storage Solutions Offer Optimal Data Protection?
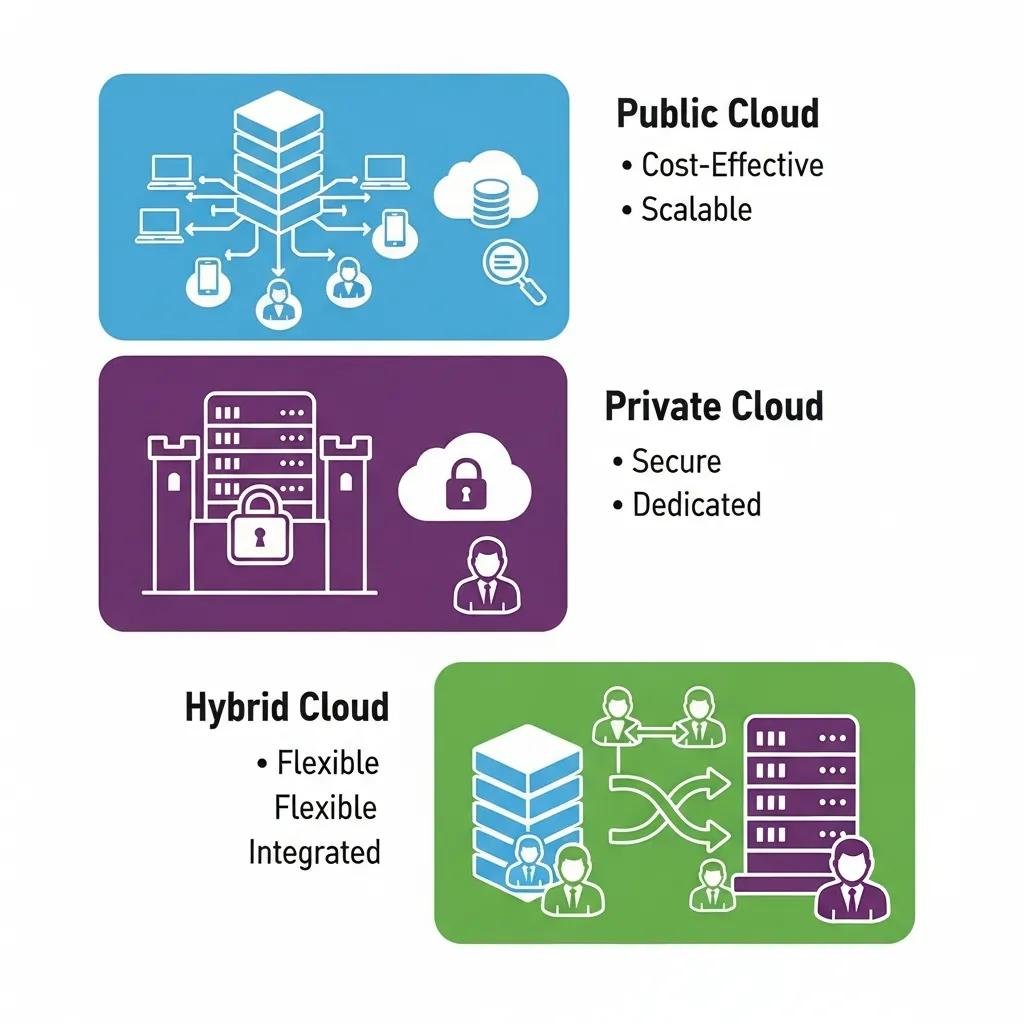
Choosing a secure cloud storage approach requires balancing control, scalability, compliance, and cost while validating provider features that protect data. Public, private, and hybrid storage models each offer distinct trade-offs: public cloud provides managed security and scale, private cloud grants direct control for compliance, and hybrid combines both for staged migration or sensitive workloads. Below is a compact comparison to help map storage choices to protection needs and operational constraints.
When evaluating providers, focus on these differentiators:
- Encryption options and the ability to use customer-managed keys.
- Access controls, identity integration, and audit log transparency.
- Compliance certifications, data residency options, and SLA-backed durability.
| Storage Model | Protection Attribute | Typical Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Public Cloud | Managed encryption, scalable access controls | High scalability with provider-managed security |
| Private Cloud | Direct hardware control, isolated tenancy | Strong control for compliance-sensitive data |
| Hybrid Cloud | Selective residency, integrated networking | Flexible balance of control and scale |
This comparison highlights how each storage model aligns with protection attributes and typical operational outcomes. The following H3 items expand on provider features and decision criteria for choosing among these models.
What Features Define Reliable Cloud Storage Providers?
Reliable cloud storage providers combine strong encryption, granular access control, regulatory compliance support, and resilient durability guarantees to protect data effectively. Encryption options should include both provider-side and customer-managed key choices along with transparent KMS integration. Providers must offer audit support and recognized certifications for data protection, along with redundancy and SLA terms that match business recovery objectives. Evaluate backup, snapshot, and retention capabilities, plus logging and access analytics to ensure forensic readiness. These provider features collectively reduce data exposure and support regulatory needs while enabling predictable operational recovery.
How to Choose Between Public, Private, and Hybrid Cloud Storage?
Decision criteria for selecting a storage model hinge on security needs, compliance obligations, performance requirements, and total cost of ownership. Choose public cloud when you need rapid scaling and managed security controls with minimal operational overhead. Opt for private cloud if strict data residency, tenancy isolation, or bespoke control over hardware and networking is essential. Use hybrid models to keep sensitive data on private infrastructure while leveraging public cloud for burst capacity or non-sensitive workloads. Assess trade-offs such as management complexity, integration costs, and the operational maturity required to maintain secure hybrid configurations.
What Are Effective Cloud Data Protection Strategies to Mitigate Risks?
Effective cloud data protection combines preventative measures with recoverability and rapid detection to reduce the likelihood and impact of data loss or compromise. Core strategies include immutable backup and recovery plans, continuous monitoring and logging, and a practiced incident response capability. These elements work together to ensure that data remains available and trustworthy even when incidents occur. Below are focused tactics teams should adopt to mitigate cloud-specific risks.
Key mitigation strategies include:
- Regular immutable backups with versioning and offsite retention to counter ransomware.
- Centralized monitoring and alerting through SIEM and CSPM tooling for real-time detection.
- Clear incident response plans with defined RTO/RPO targets and routine tabletop exercises.
| Strategy | Attribute | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Immutable Backups | Versioning, write-once storage | Protects against tampering and ransomware |
| Continuous Monitoring | SIEM, CSPM, log centralization | Detects configuration drift and threats early |
| Incident Response | Playbooks, testing, recovery metrics | Reduces downtime and error during remediation |
The table maps protective strategies to attributes and the practical value they deliver. Next, the H3 subsections explain how backups and monitoring specifically enhance security posture.
How Does Regular Data Backup Enhance Cloud Security?
Regular backups provide a reliable fallback that preserves data integrity and supports rapid restoration when primary datasets are lost or corrupted. Implement immutable backups and snapshot versioning to prevent tampering and to ensure historical recovery points exist after ransomware or accidental deletion. Define recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO) based on business needs, and automate backup schedules while validating restores through periodic tests. Store backups across geographically separated locations where possible to mitigate regional outages, and maintain access controls and encryption for backup stores to prevent exfiltration. Frequent testing of recovery procedures ensures that backups are usable and that teams can meet recovery targets.
What Role Does Continuous Monitoring Play in Cloud Security?
Continuous monitoring detects threats and configuration drift by analyzing telemetry from logs, events, and system metrics to trigger alerts for suspicious activity. Use CSPM to identify misconfigurations and SIEM to aggregate logs for correlation and forensic analysis; set retention policies and automated alerting thresholds that support timely investigation. Define an incident triage workflow that escalates verified anomalies to response playbooks and integrates threat intelligence for context-aware decisions. Monitoring also supports compliance reporting and audit readiness by preserving evidentiary trails. Effective monitoring shortens detection time and enables faster containment, directly reducing the window of attacker activity.
What Are the Emerging Cloud Security Trends for 2025?
Emerging trends in cloud security for 2025 emphasize automation, AI-driven detection, and stronger architectural models that shift control closer to identity rather than network perimeter. Organizations are adopting Zero Trust principles, expanding managed security services, and integrating machine learning to prioritize alerts and automate remediation of common misconfigurations. Regulatory attention continues to push providers and customers toward better data residency controls, more transparent encryption options, and standardized auditability. These shifts influence how teams design defenses and select tooling to protect secure cloud data going forward.
Emerging trends to watch:
- AI/ML for anomaly detection, threat prioritization, and automated remediation.
- Broader Zero Trust adoption, focusing on identity-first controls and micro-segmentation.
- Increased market demand for managed security services and compliance-focused tooling.
How Will AI and Machine Learning Impact Cloud Security?
AI and machine learning will augment detection capabilities by identifying anomalous patterns across large telemetry volumes, reducing alert fatigue and surfacing novel threats that signature-based systems miss. ML-driven models can prioritize high-risk incidents and enable automated remediation for straightforward misconfigurations, but they require high-quality telemetry and ongoing tuning to limit false positives. Human oversight remains necessary to validate model outputs and handle complex adversarial scenarios, while explainable ML approaches help security teams trust automated decisions. As tooling matures, organizations that integrate AI thoughtfully will improve MTTR and reduce manual triage overhead.
What Are the Predictions for Cloud Security Market Growth?
Market trends point toward greater investment in managed cloud security services, consolidation of tooling around integrated platforms, and rapid expansion of AI-enabled security offerings to meet scale demands. Organizations will increasingly outsource specialist functions like continuous monitoring and incident response to providers that can deliver operational maturity and compliance support. This shift implies more standardized security stacks, emphasis on tooling that supports data residency and governance, and a competitive landscape where automation and integration become key differentiators. As a result, security teams should prioritize architectures and processes that leverage managed services and automation while maintaining clear control over identity and cryptographic keys.