Using Windows Game Mode to Boost Gaming Performance: How to Enable and Optimize for Better FPS
Windows Game Mode is a built-in OS feature that helps prioritize gaming workloads by reducing background activity and focusing CPU/GPU resources on the active game, and it can improve frame-rate consistency and input responsiveness on many systems. This article explains what Game Mode does, how Windows 10 and Windows 11 expose the feature, and when enabling it yields measurable FPS or latency benefits versus negligible change. You will learn step-by-step how to enable Game Mode in Windows 11, what related toggles like the Game Bar and Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling do, and how to test improvements safely. The guide also addresses common myths about Game Mode’s effectiveness and provides practical optimization steps that go beyond the toggle—drivers, power plans, and background process control. Finally, we’ll cover signs that indicate a deeper issue where remote professional optimization can help, and point to remote services that specialize in computer speed-up and optimization for stubborn performance problems.
What is Windows Game Mode and How Does It Improve Gaming Performance?
Windows Game Mode is a feature in the Windows operating system designed to reduce interruptions and allocate resources to the foreground game, improving stability and sometimes increasing FPS. It works by minimizing background CPU usage, limiting background tasks, and nudging the scheduler to favor gaming threads so the GPU and CPU can maintain steadier frame delivery. The specific benefit is often smoother frame pacing and reduced stutter rather than large increases in peak FPS, especially on systems bogged by background services. Understanding these mechanisms makes it easier to decide when Game Mode will help and when other optimizations will be more effective.
Game Mode’s effect depends on system load and game architecture, so complementary steps usually improve results.
Understanding Game Mode Features in Windows 10 and Windows 11

Game Mode appears in Settings under Gaming on both Windows 10 and Windows 11, but UI locations and default behaviors vary slightly between releases. In Windows 11 the path is Settings → Gaming → Game Mode where a single toggle enables system-level prioritization, while Windows 10 exposes similar controls and ties Game Mode more directly to the Game Bar and Xbox services. Compatibility differs across titles: some games signal themselves to the OS accurately and get full prioritization, while older or exclusive-fullscreen titles may behave differently. Knowing the OS path and compatibility helps you confirm Game Mode is active during a session.
These version differences lead to practical configuration steps you can take to test whether enabling Game Mode helps your specific setup.
How Game Mode Prioritizes System Resources for Gaming
Game Mode influences scheduler behavior and background task management by reducing priority for non-essential services and focusing resources on the active gaming process, which often improves frame timing and reduces latency spikes. Practically, this translates to fewer CPU-bound background tasks, reduced I/O interference from indexing or updates, and slightly better thread scheduling for game processes. However, if the GPU or CPU is already saturated by the game, Game Mode cannot overcome hardware limits and measurable FPS gains will be minimal. Recognizing when Game Mode is likely to help—systems with many background apps or lower-core CPUs—guides whether to rely on it or pursue driver and power-plan changes.
That distinction leads directly into how to enable Game Mode and which related settings to test alongside it.
How to Enable and Configure Windows Game Mode Settings for Optimal Gaming
Enabling Game Mode is a quick first step for many players and should be done alongside targeted testing to validate improvements, since the feature’s impact varies by system and title. The following numbered steps give a concise HowTo for Windows 11 and map each action to an expected result so you can measure changes. After enabling Game Mode, test with a repeatable benchmark or the game’s built-in FPS counter and compare frame-time consistency before and after.
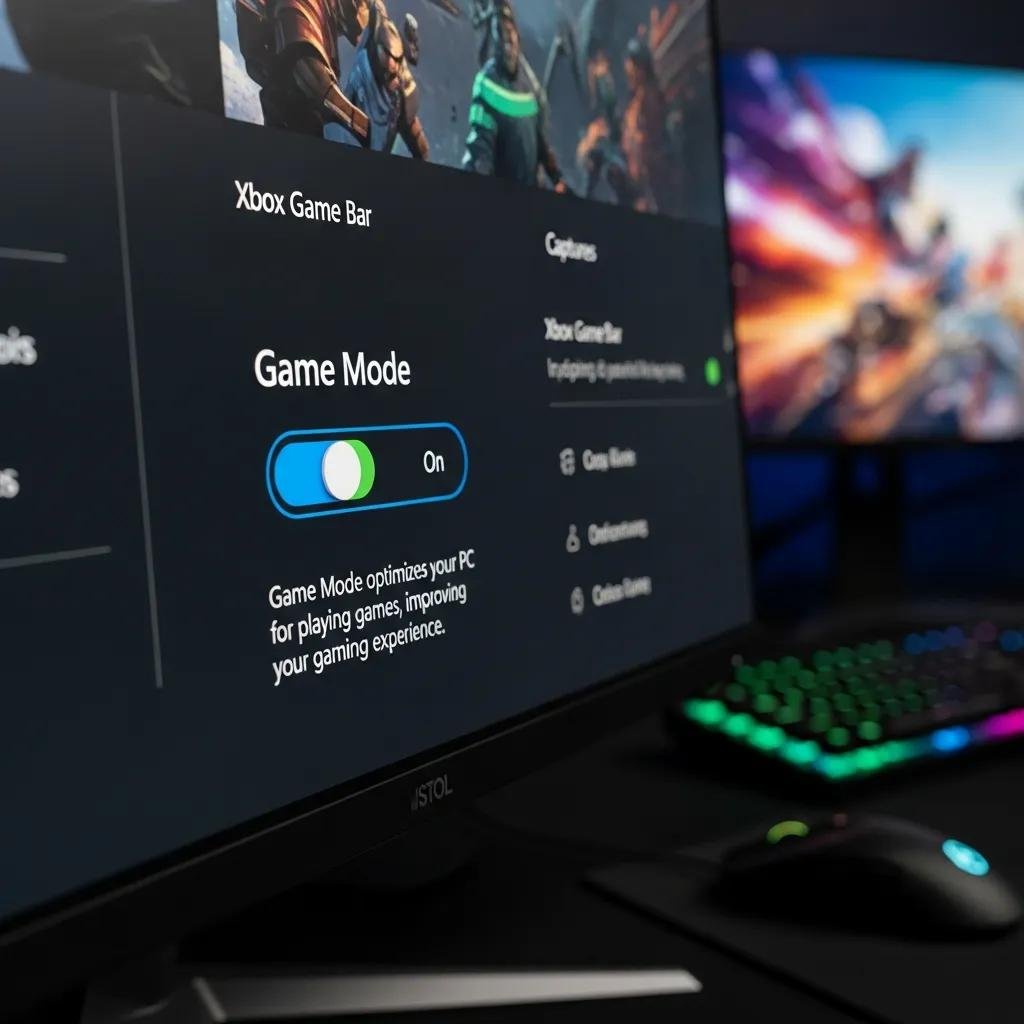
- Open Settings → Gaming → Game Mode and toggle Game Mode on; expected result: OS reduces background CPU scheduling during detected gameplay.
- Open Settings → Gaming → Xbox Game Bar and disable overlays/recording if you notice capture-related frame drops; expected result: lower overhead from background recording.
- Check Graphics settings and consider enabling or disabling Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling to test driver-specific benefits; expected result: minor latency or frame-time improvements on supported drivers.
These steps create a baseline for controlled A/B testing to confirm whether Game Mode and related toggles help in your environment.
Intro to the configuration table below explains which step produces which immediate, observable change.
| Setting / Feature | Action Step | Likely User-Visible Result |
|---|---|---|
| Game Mode toggle | Settings → Gaming → Game Mode → On | Reduced background CPU tasks; improved frame consistency |
| Xbox Game Bar recording | Settings → Gaming → Xbox Game Bar → Disable recording | Less CPU/GPU overhead from capture; fewer stutters |
| Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling | Settings → System → Display → Graphics settings | Minor latency/frame-time improvement on supported drivers |
Summary: use the table to map each configuration change to what you should expect during testing, then validate with simple benchmarks.
Step-by-Step Guide to Enable Game Mode in Windows 11
Follow these concise numbered instructions to enable Game Mode in Windows 11 and verify activation quickly. First, press to open Settings, then choose Gaming and select Game Mode; switch the toggle to On and note the setting’s state. Next, launch your target game and check whether Windows shows Game Bar or overlay indicators; Game Mode activates automatically when a supported title runs in the foreground. Finally, run a short benchmark or built-in FPS overlay for 3–5 minutes to collect baseline numbers for comparison.
After confirming activation, proceed to turn related overlays or scheduling features on/off to measure incremental impact.
Adjusting Related Settings: Game Bar and Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling
The Game Bar provides overlays, capture, and performance widgets, but recording and overlays can introduce CPU or GPU overhead that offsets Game Mode benefits; disabling capture can reduce that overhead. Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling is a newer Windows option that moves some scheduling tasks to GPU drivers and the GPU itself; on certain drivers it yields small latency or frame-time wins but on others it can introduce instability. The recommended approach is A/B testing: disable the Game Bar recording and toggle GPU scheduling while running controlled bench or in-game tests, then compare median FPS and 99th-percentile frame-times.
Testing these settings in sequence isolates which change produced improvement and prevents wasted tinkering.
Does Windows Game Mode Really Work? Myths, Facts, and Performance Impact
Game Mode works in many real-world cases to improve frame consistency and reduce interruptions, but its ability to increase peak FPS is limited and highly system-dependent. Common myths claim dramatic FPS increases or that Game Mode replaces proper driver and hardware maintenance; the reality is that Game Mode is a resource-prioritization layer that helps when background activity or OS services are the bottleneck. Recent testing and community benchmarks indicate modest average FPS changes but notable improvements in stutter and frame-time variance on loaded systems. Below is a compact summary table comparing claims against typical evidence to help you set expectations before deep optimization.
| Feature | Typical Impact on FPS | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Game Mode | Modest average FPS change; improved consistency | Systems with heavy background tasks |
| Game Bar recording | Can reduce FPS when enabled | Casual capture; disable for competitive play |
| Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling | Minor improvements on select drivers | Newer GPUs with up-to-date drivers |
Common Misconceptions About Game Mode Effectiveness
Several misconceptions surround Game Mode, including that it guarantees large FPS gains or that it substitutes for hardware or driver issues, but these beliefs overstate its scope. Reality is that Game Mode helps primarily by limiting background interference and improving thread scheduling; it cannot increase a GPU’s raw throughput or fix outdated drivers. Another myth is that Game Mode is always on or always beneficial — it must be enabled and tested per title to confirm benefits. Correcting these misconceptions helps prioritize appropriate troubleshooting steps like driver updates or power-plan changes when Game Mode appears ineffective.
Understanding limits leads to realistic testing strategies for measurable results.
Real-World FPS and Latency Improvements with Game Mode
In practice, users report small FPS uplifts (single-digit percent) in some games and clearer reductions in frame-time spikes when background processes were previously interfering. Latency and input responsiveness often improve more through reduced jitter than through a higher maximum FPS, which matters for competitive play where consistency is key. To measure effects accurately, use tools like built-in counters, third-party frametime loggers, or simple file-based repeatable benchmarks and compare median and 99th-percentile timings. If measurements show little to no change after enabling Game Mode and adjusting overlays, deeper optimizations or professional diagnostics are the appropriate next step; persistent issues beyond Game Mode’s scope may require remote optimization services for driver conflicts and system cleanup.
For persistent problems, consider professional remote help that specializes in computer speed-up and optimization.
How to Optimize Windows Beyond Game Mode for Maximum Gaming Performance

Beyond Game Mode, performance gains are most often achieved by updating graphics drivers, selecting the right power plan, and controlling background apps and startup services. Start by ensuring GPU and chipset drivers are fresh and use clean-install options when switching major driver families, since driver conflicts often cause stutters and crashes. Next, choose a high-performance power plan or the Ultimate Performance profile on capable systems to prevent aggressive core parking and power-saving that throttles gaming performance. Finally, audit startup apps and background services, disable unnecessary indexes or scheduled scans, and prefer SSD storage for game installs to reduce I/O-induced hitches.
These steps build on Game Mode’s scheduling improvements and often deliver larger, more consistent gains.
Advanced Windows Settings: Power Plans, Drivers, and Background Apps
Configuring Windows power profiles and keeping drivers current are critical steps that complement Game Mode and can produce measurable FPS and stability improvements. Switch to a High Performance or Ultimate Performance plan depending on hardware and power constraints, and configure processor power management to avoid deep C-states during gameplay. Update GPU drivers from your vendor and use custom clean-install options when available, and keep chipset and storage firmware current. Finally, manage background apps via Task Manager and Settings to prevent CPU and disk contention while gaming.
Start with drivers and power settings, then move to background app control to compound benefits.
When to Seek Professional PC Optimization Services for Gaming
If you encounter persistent low FPS, random crashes, driver conflicts, or complex stability problems that do not resolve after Game Mode and standard tweaks, remote professional optimization can diagnose root causes more efficiently. Remote services that focus on computer speed-up and optimization can run in-depth diagnostics, perform clean driver installs, resolve driver conflicts, and perform targeted cleanup of services and scheduled tasks that degrade performance. mcHelper.com operates as a remote computer repair and technical support service that offers computer speed-up and optimization, remote support from home or office, 24/7/365 specialist availability, a no fix–no fee promise, and an annual subscription option for ongoing maintenance; use professional help when systematic troubleshooting is not restoring performance.
Professional intervention is the natural next step when DIY changes fail to restore consistent gaming performance.